 Diter Oy has manufactured devices intended for electrophysical modalities and developed treatment methods and protocols since 1976. Electrophysical modalities may provide help and relief for a variety of musculoskeletal problems. The aim of the treatments is to relieve pain and promote the restoration of functional capacity. Treatments are given as a series of several sessions, in which the aim is to carry out the treatments daily.
Diter Oy has manufactured devices intended for electrophysical modalities and developed treatment methods and protocols since 1976. Electrophysical modalities may provide help and relief for a variety of musculoskeletal problems. The aim of the treatments is to relieve pain and promote the restoration of functional capacity. Treatments are given as a series of several sessions, in which the aim is to carry out the treatments daily.
In 2011–2020, Diter/Diter Fysio did a follow-up of the number of treatments administered for different treatment areas and diagnoses. The follow-up included 1,096 participants who had sought an appointment with a physiotherapist on their own initiative due to their ailment.
Treatments
Of the electrophysical modalities, three-period monophase modulated current was used as the primary and main treatment during the follow-up period. In some cases, other forms of electric current, laser therapy, ultrasound and magnetic therapy were also used as complementary therapies. The choice of treatment was made on a case-by-case bases based on the diagnosis.
During the treatment period, patients were advised to avoid exercise therapy, manual therapy, strength training, and anti-inflammatory medications. The goal was to make the treated area pain-free, after which other treatment methods and exercises were introduced, among other things, to prevent recurrence of the condition.
Treatment frequency
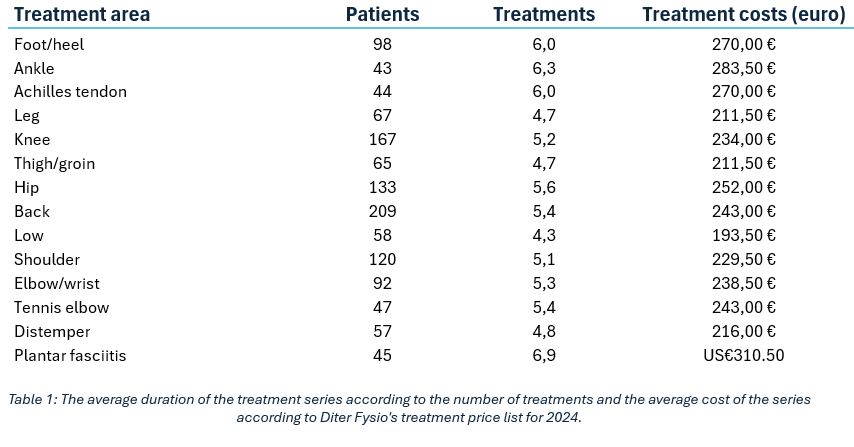
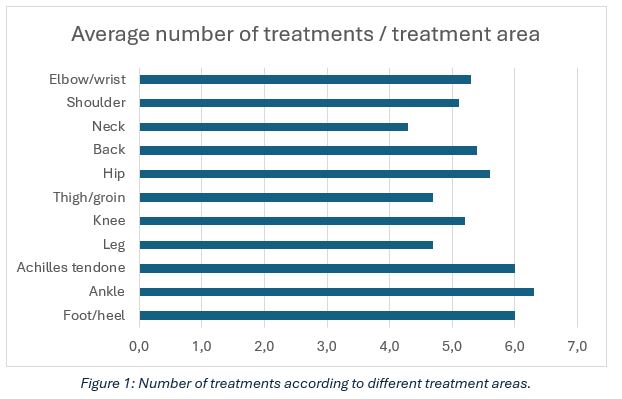
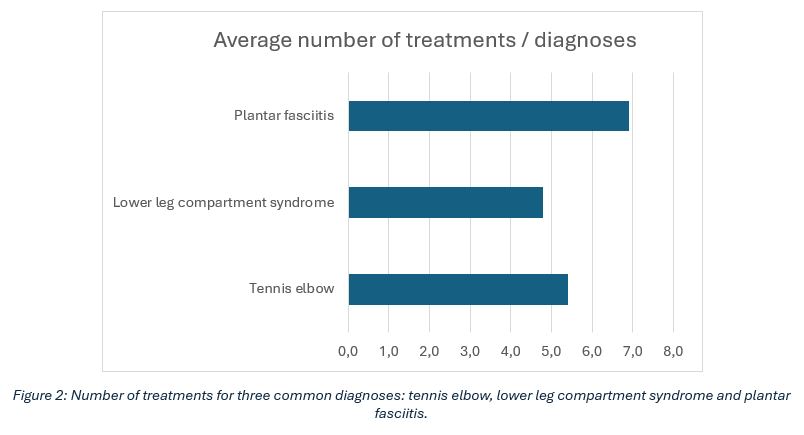
During the follow-up period, the average number of treatment sessions per patient was found to be 5.3, resulting in an average cost of approximately 240 euros per patient (Table 1, Figures 1–2). In terms of time, this means a treatment period lasting approximately one week.
The treatment targets described above included, among others, the following diagnoses:
- Foot/heel: plantar fasciitis, apophysitis of the heel bone (Sever's ailment), foot fracture, heel bursitis, nerve compression of the foot (Morton's neuroma)
- Ankle: ankle pain, sprain, fracture
- Achilles tendon: inflammation
- Shin: lower leg compartment syndrome
- Knee: Osgood-Schlatter disease, jumper's knee, Baker's cyst, runner's knee
- Thigh: muscle spasm, pain, contusion, muscle tear, wooden leg, fracture
- Hip: pain, bursitis, piriformis syndrome, ischial tuberosity pain
- Back: lower back pain, SI joint pain, quadratus lumborum pain, herniated disc
- Neck: various neck-shoulder pain conditions
- Shoulder: tendonitis (infraspinatus, supraspinatus)
- Elbow/wrist: tendonitis (lateral/medial epicondylitis i.e. tennis/golfer's elbow), wrist pain
Post-treatment
There was no need to repeat the treatment series for the same condition during the follow-up period.
